序号:01
地理坐标:E102° 32' 10.111",N31° 1' 48.544"
地质时期:晚三叠世卡尼期、诺利期、瑞替期
地学价值类型:构造与构造地质学
重要性等级:世界级
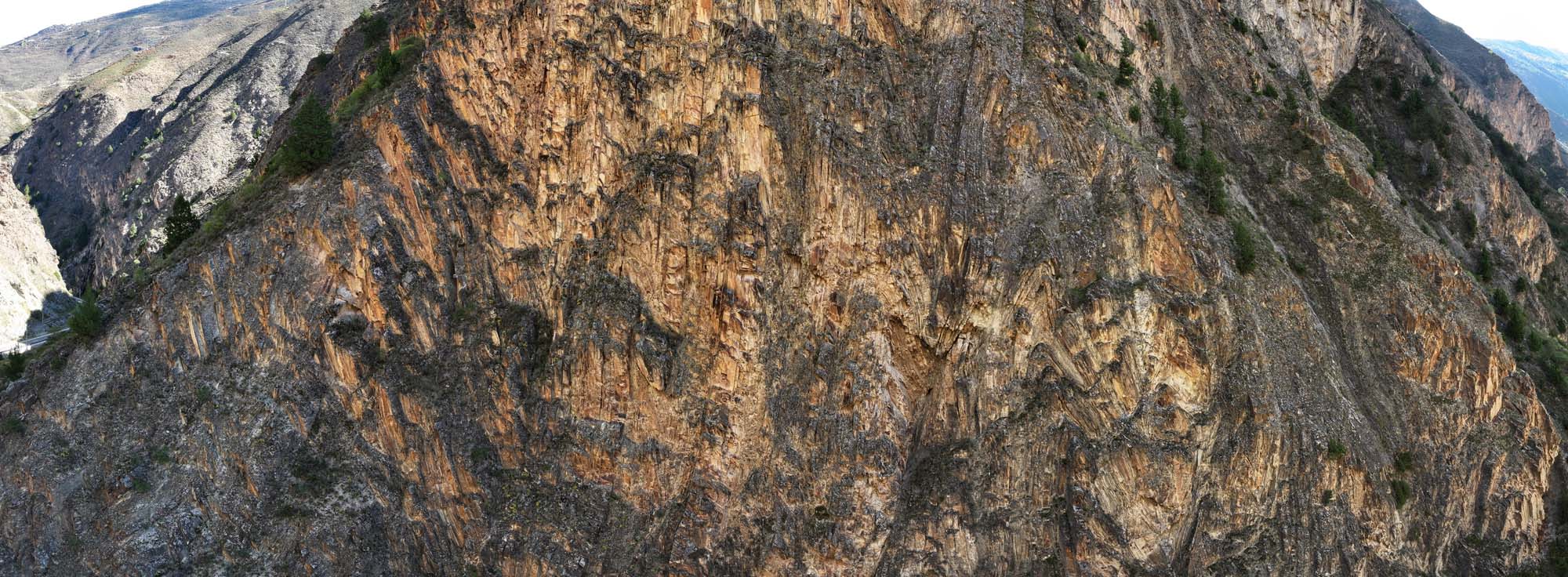
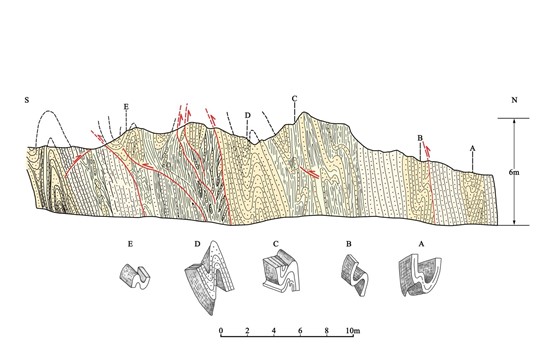
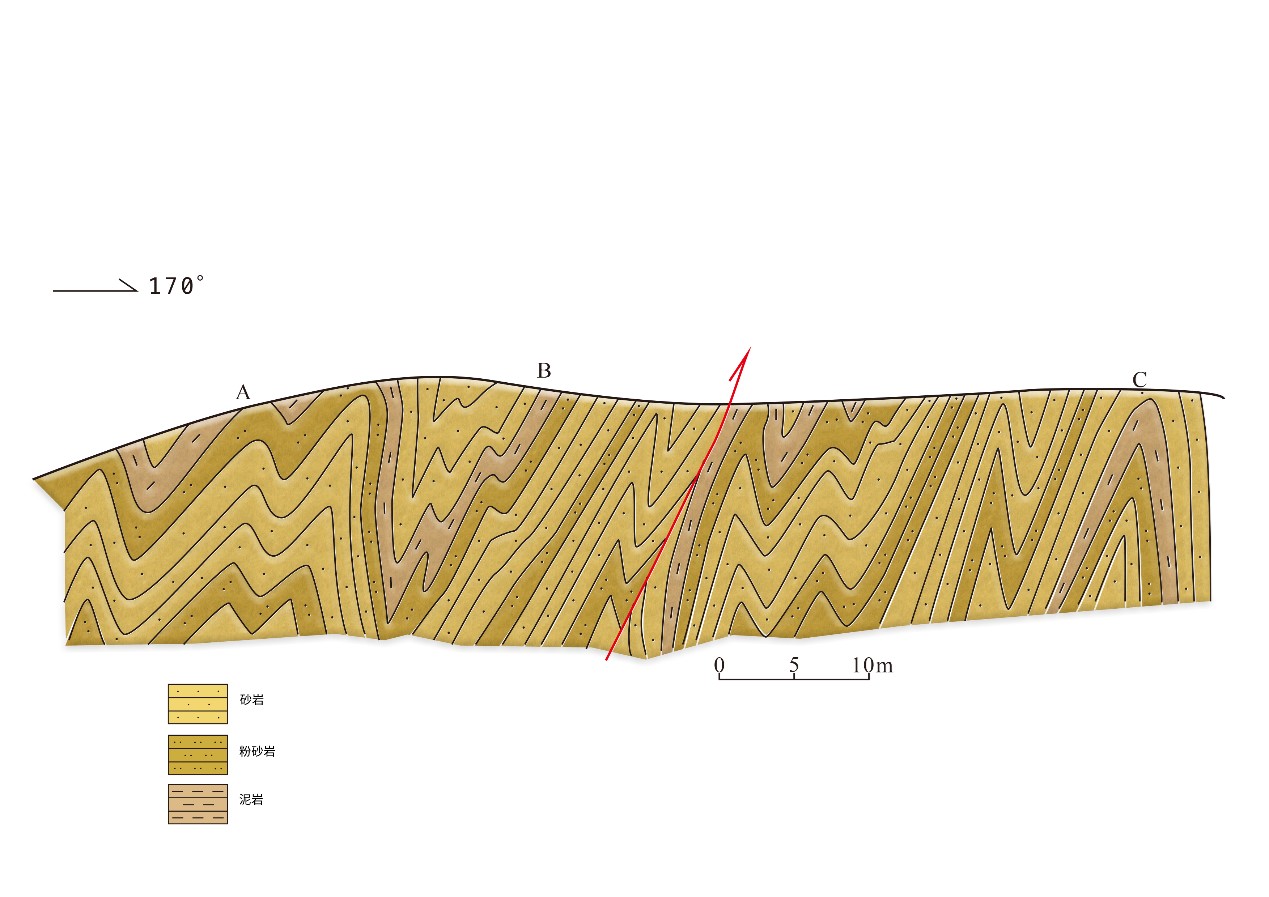
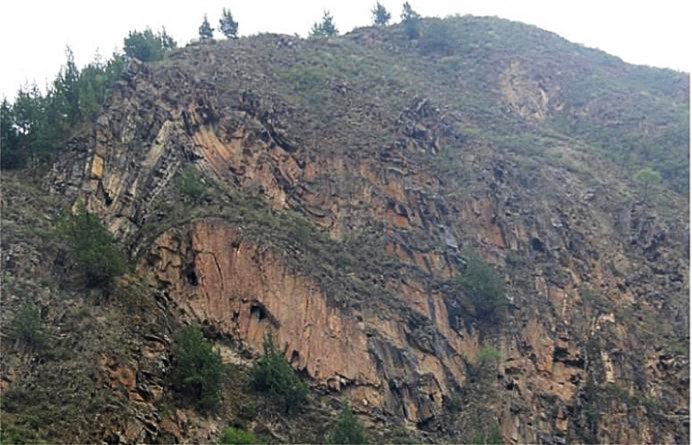
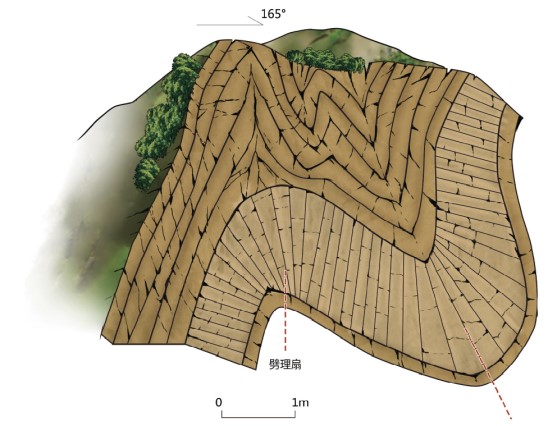
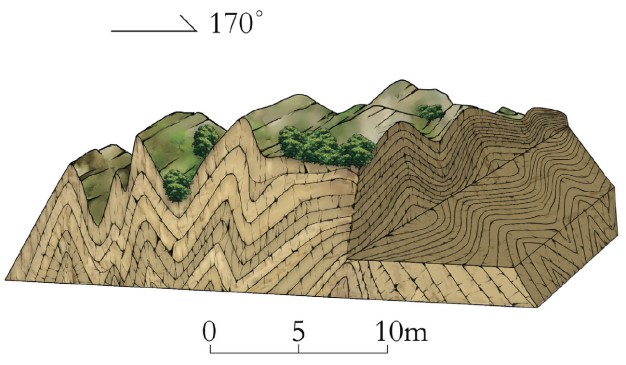
地质遗迹点描述:位于结斯沟口的沟谷两侧坡壁上,褶皱形态清晰,数量丰富,类型多样,主要有尖棱褶皱、紧闭直立褶皱、倒转褶皱、平卧褶皱、叠置褶皱等,另外还可见线理构造和面理构造、杆状构造等,可以称为“天然褶皱构造博物馆”,是中国科学院院士许志琴研究与命名“西康式”褶皱的模式地。
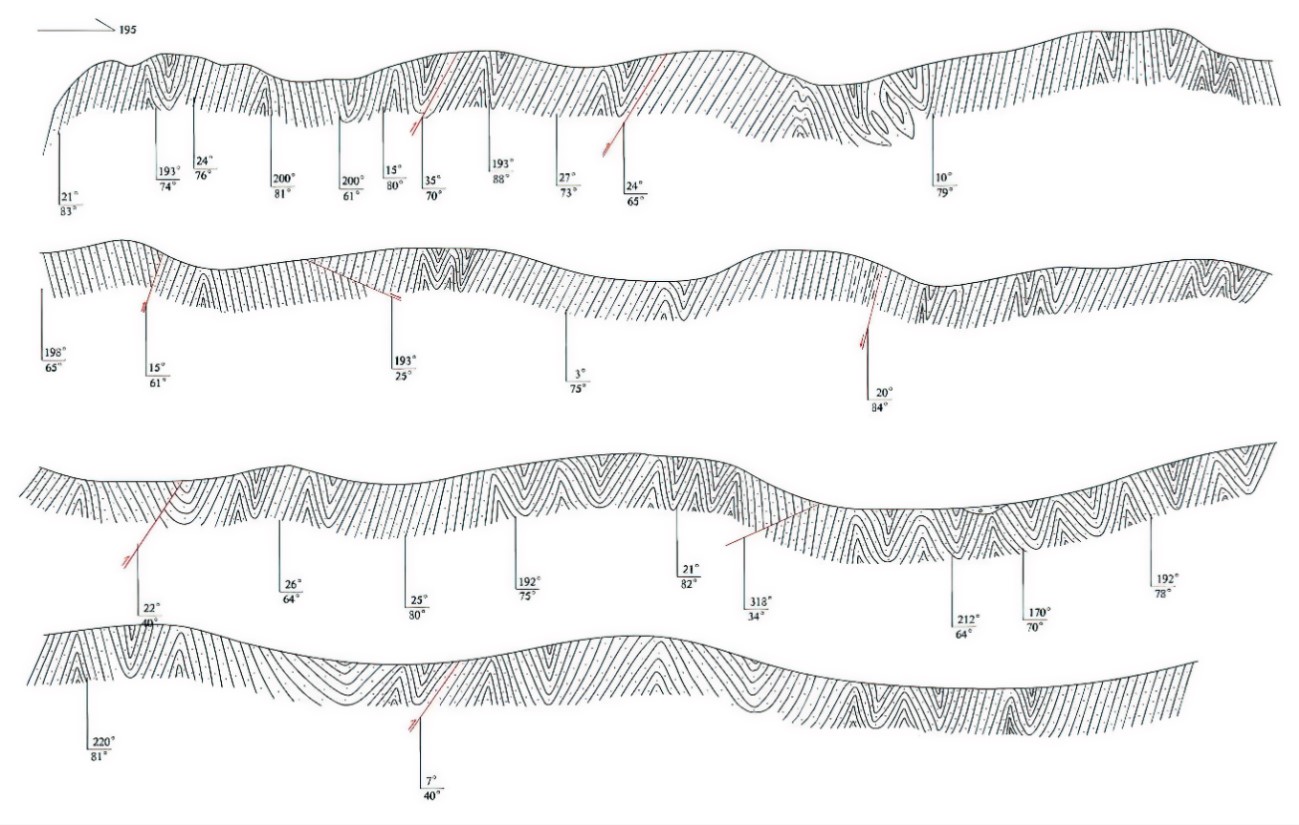
“西康式”褶皱是一种同劈理直立褶皱,广泛发育在由巨厚砂板岩组成的“西康群”复理石岩系中,“西康式”褶皱推测形成深度为10~15km。它的突出特点表现为:褶皱枢纽倾状角是变化的、倾伏向也是变化的;具有较紧闭-紧闭的圆滑-同心褶皱、尖棱褶皱及过渡型褶皱等多种复合褶皱形式;由不同类型劈理构成复杂的折射劈理图形;在流劈理面上发育有垂直的拉伸线理。
结斯沟上三叠统侏倭组砂岩的变形构造剖面,表明了劈理面走向稳定(NWW290°~304°),但褶皱枢纽倾伏角有很大变化,表明它是一种叠置褶皱,其形成需要一个近南北向延伸及倾角变化的面理(层理或劈理)作为基础,是发育在造山带内部复杂应力作用的产物。
世界级价值的明确理由:公园是“西康式”褶皱的模式地,“西康式”褶皱是松潘-甘孜造山带陆内造山的产物。松潘-甘孜造山带处于扬子地块、华北地块、柴达木地块和羌塘地块之间,东临四川盆地,其北侧为昆仑-阿尼玛卿缝合带,南侧为甘孜-理塘缝合带和金沙江缝合带,东侧为龙门山逆冲推覆构造带。不同于世界上多数线形造山带,松潘-甘孜造山带呈“楔形”,是双向挤压陆-陆碰撞造山的突出例证,也是一种全新的造山带类型。中国科学院许志琴院士发表的《中国松潘-甘孜造山带的造山过程》中详细论证其科学价值。发育于松潘-甘孜造山带的“西康式”褶皱是一种同劈理直立叠置褶皱,其在构造特征、形成机制及壮观程度上,完全可与世界著名的“侏罗山式”“彭尼内式”造山带褶皱对比,是造山带中一种独特的褶皱类型。

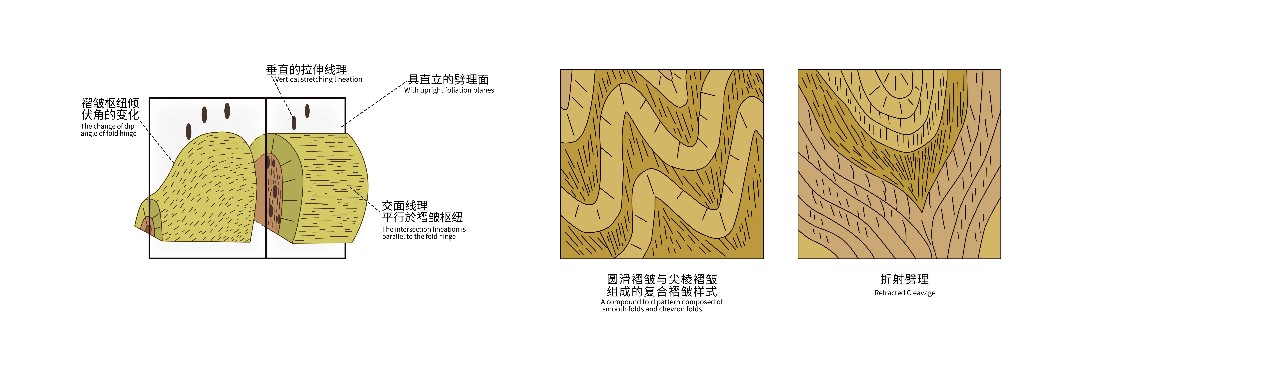
A “西康式”褶皱

B 扇形劈理
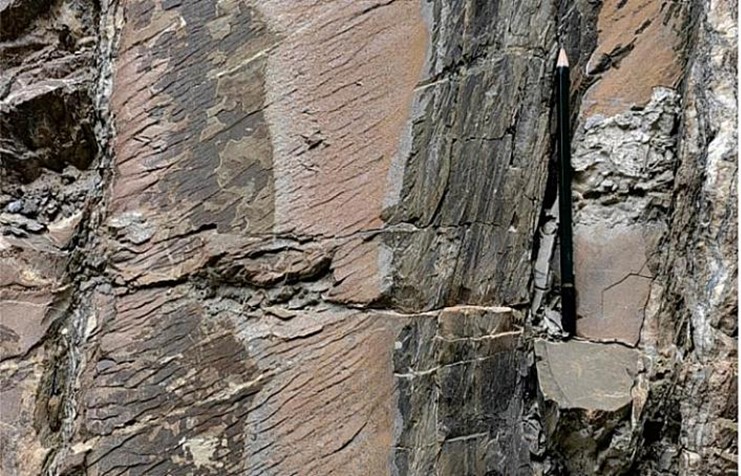


C 折射劈理

D 褶皱立体解剖图
代表性文献:
a) Yuan, C., Zhou, M. F., Sun, M., Zhao, Y., Wilde, S., Long, X., & Yan, D. (2010). Triassic granitoids in the eastern Songpan Ganzi Fold Belt, SW China: Magmatic response to geodynamics of the deep lithosphere. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 290(3-4), 481-492.
b) Zhang, H. F., Zhang, L., Harris, N., Jin, L. L., & Yuan, H. (2006). U–Pb zircon ages, geochemical and isotopic compositions of granitoids in Songpan-Garze fold belt, eastern Tibetan Plateau: constraints on petrogenesis and tectonic evolution of the basement. Contributions to Mineralogy and Petrology, 152, 75-88.
c) Huang, M. H., Buick, I. S., & Hou, L. W. (2003). Tectonometamorphic evolution of the eastern Tibet plateau: Evidence from the central Songpan–Garzê orogenic belt, Western China. Journal of Petrology, 44(2), 255-278.
d) Harrowfield, M., & Wilson, C.J. (2005). Indosinian deformation of the Songpan Garzê Fold Belt, northeast Tibetan Plateau. Journal of Structural Geology, 27, 101-117. 3.1
e) Haoyu Yan, Zhiqin Xu, Guangwei Li, Bihai Zheng, Jianguo Gao, Xiaoping Long; Whole-Rock and Apatite Geochemistry of Late Triassic Plutonic Rocks in the Eastern Songpan-Ganzi Orogenic Belt: Petrogenesis and Implications for Tectonic Evolution.
f) Danping YAN, Meifu ZHOU, Guoqin WEI, He LIU, Tiezhu DONG, Weichen ZHANG, Zhelong JIN, Collapse of Songpan-Garzê orogenic belt by a Mesozoic middle-crustal ductile channel flow: evidences from deformation and metamorphism within the Sinian-Paleozoic strata in the hinterland of Longmenshan foreland thrust belt, Earth Science Frontiers,Volume 15, Issue 3, 2008,Pages 186-198.
g) Liu, S., & Wang, Y. (2023). Origin of the Songpan-Garze Terrane on the northeastern Tibetan Plateau, eastern segment of the Tethyan tectonic domain: A Middle Permian–Early Triassic intracontinental rifting system. Bulletin, 135(7-8), 1993-2014.
h) Roger, F., Jolivet, M., & Malavieille, J. (2010). The tectonic evolution of the Songpan-Garzê (North Tibet) and adjacent areas from Proterozoic to Present: A synthesis. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 39(4), 254-269.
i) Roger, F., Malavieille, J., Leloup, P. H., Calassou, S., & Xu, Z. (2004). Timing of granite emplacement and cooling in the Songpan–Garzê Fold Belt (eastern Tibetan Plateau) with tectonic implications. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 22(5), 465-481.
j) Xu, Z.-q., Hou, L.-w., Wang, D.-k., & Wang, Z.-x. (1991). “Xikang-type” folds and their deformation mechanism: A new fold type in orogenic belts. Geological Bulletin of China, (1), 1-9.

