Legal framework
Mt. Siguniang National Nature Reserve Administration bears the legal responsibility for managing the geopark and implements regulations within the Mt. Siguniang Geopark. According to national laws such as the Constitution of the People’s Republic of China, the Environmental Protection Law of the People’s Republic of China, the Mineral Resources Law of the People's Republic of China, the Forest Law of the People's Republic of China, the Regulations of the People’s Republic of China on the Nature Reserves, the Regulations on the Protection of Paleontology Fossils, and the Regulations on the Protection of Geological Heritages, as well as local regulations such as the Sichuan Provincial Environmental Protection Regulations, the Sichuan Provincial Geological Environment Management Regulations, and the Sichuan Provincial Wetland Protection Regulations, Mt. Siguniang Geopark and all its geological heritages are strictly protected by law. Currently, the integrity of the geological heritages in the geopark is well-preserved.
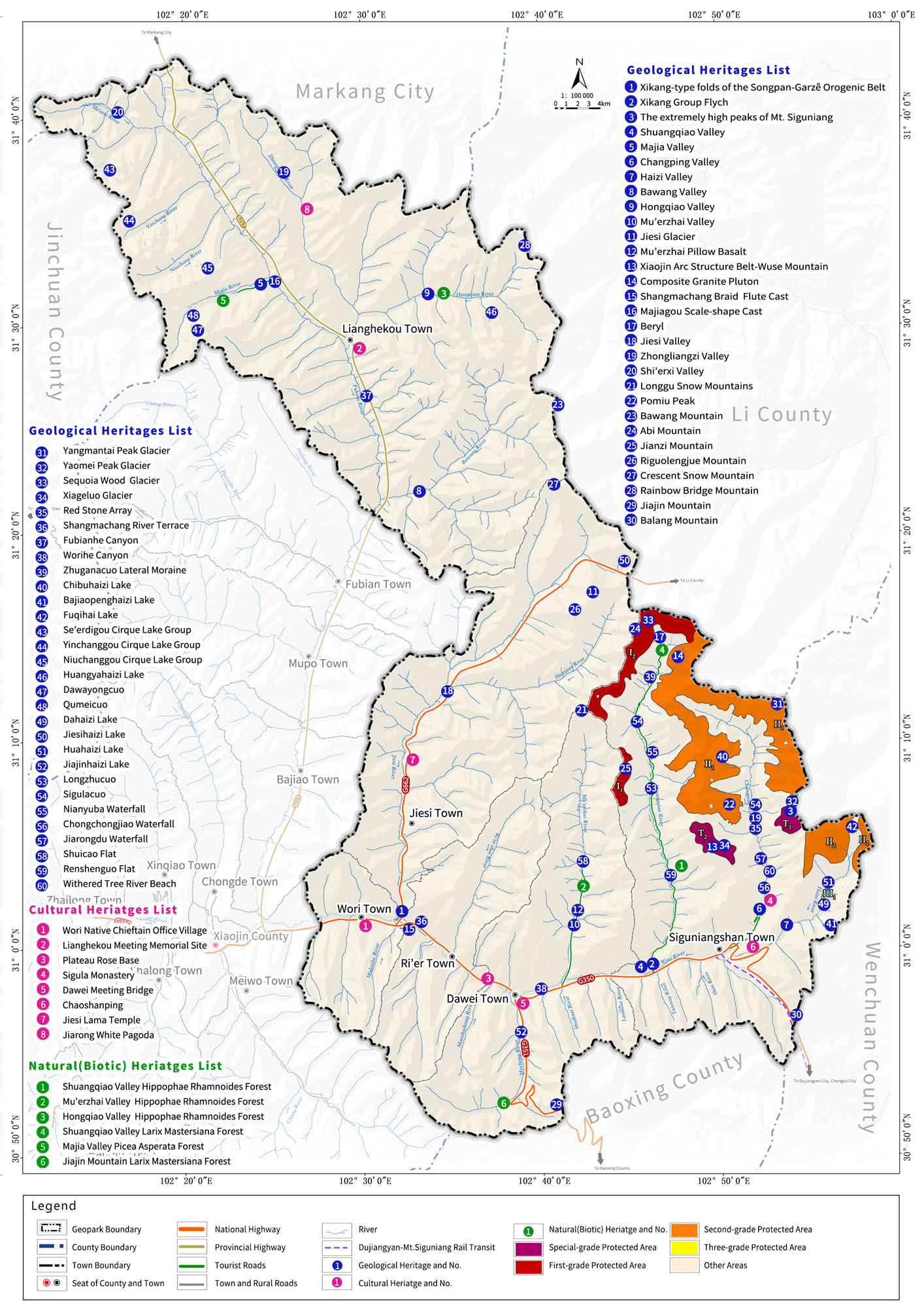
Geological heritage protection zoning and measures
Mt. Siguniang Geopark classifies its protection zones based on the rarity and aesthetic value of geological sites into Special Protection Zones, Grade I Protection Zone, Grade II Protection Zone, and Grade III Protection Zones (Points). Special Protection Zones are off-limits to tourists. Only personnel approved by the Geopark management for protection and research purposes can enter. No buildings or facilities unrelated to geological heritages protection are allowed within these zones. Grade I Protection Zones may have necessary viewing trails and related facilities, but they must harmonize with the landscape environment. The number of visitors is strictly controlled, and motor vehicles are prohibited. Grade II Protection Zones allow for a small number of geological tourism service facilities that must coordinate with the landscape environment. Construction that impacts the geological heritages’ landscape is not permitted. Visitor numbers are reasonably controlled. Grade III Protection Zone (Points) can have an appropriate number of geological tourism service facilities that harmonize with the landscape environment. Large-scale buildings such as halls, pavilions, and amusement facilities are not allowed.
Measures for geoheritage protection and maintenance
1.Protection of Geological Sections, Structures, and Mineral Deposits: Establish boundary markers and signage to prohibit close contact by visitors. Mineral deposits can be sampled and displayed in museums, while the original sites should be isolated and strictly protected to prevent theft, mining, and damage. 2.Protection of Rocks, Glaciers, Fluvial Landforms, and Structural Landforms: Generally, entry is restricted. However, for tourism development, controlled access for investigation and sightseeing may be permitted under safe conditions. Designated routes or platforms in nearby safe areas can be arranged for tourists to view these features. 3.Protection of Water Landscapes: Strictly control visitor access. Activities such as rafting can be organized in planned sections while ensuring the river's water quality remains uncontaminated. The ecological environment surrounding the water landscape should be protected to prevent pollution. 4.Improvement of Planning Documentation: Compile the “Overall Plan for Mt. Siguniang Geopark (2024-2035)” and the associated planning manual to clearly delineate protection boundaries. 5.Strengthening the Protection Team: The geopark has established the “Patrol System of Mt. Siguniang Geopark” and arranges dedicated personnel to regularly patrol geological sites as per the system's requirements. Any issues discovered are promptly reported and addressed. Training for patrol personnel is provided to enhance their capabilities and understanding of geological sites.